♥ Get more apps
Genetic Decoder
Nucleobases
Also know as nucleotide bases/nitrogenous bases. Nucleobases are the parts of DNA and RNA that may be involved in pairing. The primary nucleobases are cytosine, guanine, adenine (DNA and RNA), thymine (DNA) and uracil (RNA), abbreviated as C, G, A, T, and U, respectively. They are usually simply called bases in genetics.Choose a base to see details
A
T
C
G
U
Adenine
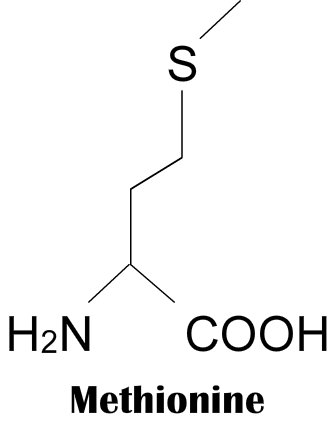
 is a nucleobase (a purine deriva-tive) with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. It is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.
is a nucleobase (a purine deriva-tive) with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. It is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.
 is a nucleobase (a purine deriva-tive) with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. It is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.
is a nucleobase (a purine deriva-tive) with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. It is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.


© biocourseware.com & touchapp.co.uk Email: [email protected]
 is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters T. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. In RNA, thymine is replaced with uracil in most cases. In DNA, thymine(T) binds to adenine (A) via two hydrogen bonds, thus stabilizing the nucleic acid structures.
is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters T. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. In RNA, thymine is replaced with uracil in most cases. In DNA, thymine(T) binds to adenine (A) via two hydrogen bonds, thus stabilizing the nucleic acid structures.
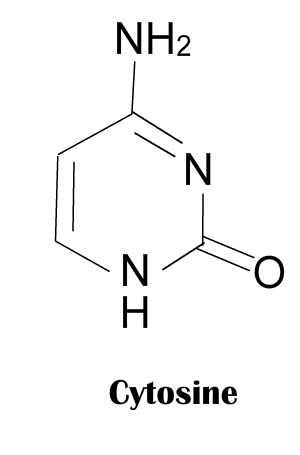 is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclicaromatic ring and two substituents attached (an amine group at position 4 and a keto group at position 2). Thenucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclicaromatic ring and two substituents attached (an amine group at position 4 and a keto group at position 2). Thenucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
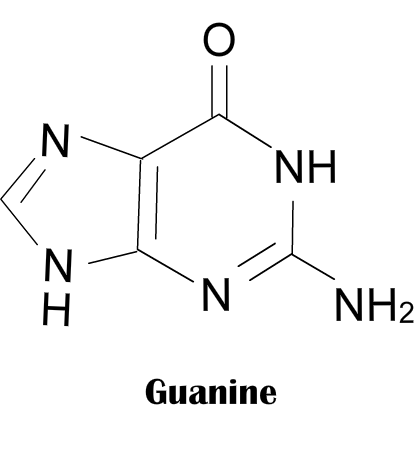 is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine.
is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine.
 is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. Originally discovered in 1900, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein that was found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light.
is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. Originally discovered in 1900, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein that was found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light.